Tanzania stands out among African nations for successfully maintaining a consistently low and stable inflation rate over the years. The National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) reports that in 2021, Tanzania’s annual inflation rate was a mere 3.69%, demonstrating a downward trend from 2020’s 3.29% and 2019’s 3.46%. These figures are remarkably below the average annual inflation rate of 15.1% recorded between 1966 and 2022. In this article, we will delve into the factors contributing to Tanzania’s impressive feat of achieving and sustaining low inflation.
1. Prudent Monetary Policy
The Bank of Tanzania (BOT) has played a crucial role in maintaining a tight monetary policy stance to ensure that inflation remains within the target range of 3-5%. Utilizing a variety of tools such as the discount rate, statutory minimum reserve ratio, and open market operations, the BOT effectively controls the money supply and influences interest rates in the economy.
2. Stable Exchange Rate
Tanzania’s currency, the shilling, has exhibited relative stability against major currencies like the US dollar, euro, and British pound. This stability significantly reduces imported inflation, which refers to price increases resulting from a decline in the domestic currency’s value.
3. Low Food Inflation
Food constitutes approximately 28% of Tanzania’s consumer price index (CPI) basket, making it the largest component of inflation. However, the country has experienced subdued food inflation in recent years, thanks to favorable weather conditions, improved agricultural productivity, and increased food supply.
4. Stable Oil Prices
Given that Tanzania is a net importer of oil and petroleum products, accounting for around 14% of the CPI basket, lower global oil prices have helped minimize production and transportation costs within the country.
5. Fiscal Discipline
The Tanzanian government has been dedicated to implementing prudent fiscal policies aimed at achieving a balance between revenue and expenditure, reducing public debt, and enhancing domestic resource mobilization. This disciplined approach mitigates the risks of excessive borrowing and spending, which could otherwise generate inflationary pressures.
Analyzing Tanzania’s Inflation Rates in Comparison from 2013
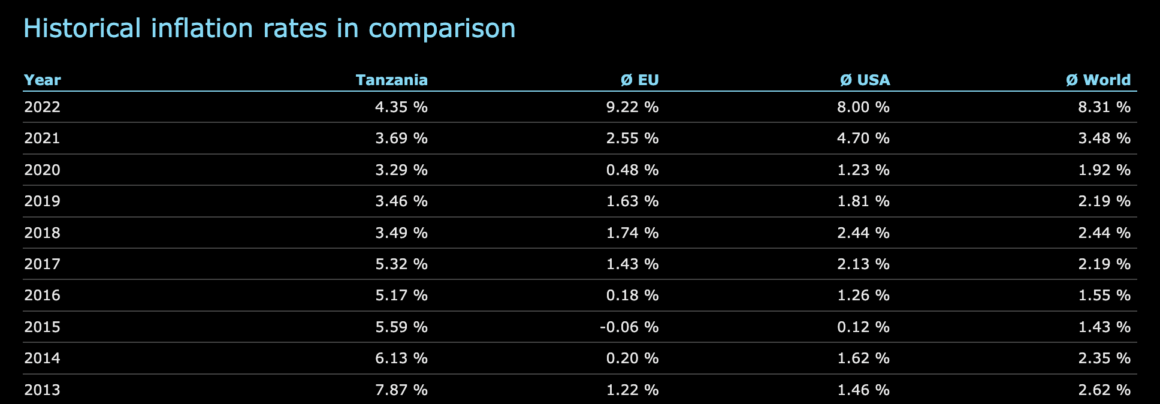
Looking at the provided data, we can discern the trajectory of Tanzania’s inflation rate over the years. While some fluctuations are evident, overall, the country has maintained a relatively stable inflation rate.
1. Comparison with EU, USA, and World:
- Tanzania vs EU: Tanzania’s inflation rate has typically exceeded the average inflation rate of the European Union.
- Tanzania vs USA: Tanzania’s inflation rate has generally been lower than the average inflation rate of the United States.
- Tanzania vs World: Tanzania’s inflation rate has varied in comparison to the global average, sometimes surpassing it and at other times falling below.
2. Inflation Rate Analysis
- 2022: Tanzania’s inflation rate stood at 4.35%, which was lower than the average inflation rates of the EU, USA, and the world.
- 2021: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 3.69%, higher than the average inflation rates of the EU and the world but lower than the USA.
- 2020: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 3.29%, higher than the average inflation rates of the EU, USA, and the world.
- 2019: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 3.46%, higher than the average inflation rates of the EU, USA, and the world.
- 2018: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 3.49%, higher than the average inflation rates of the EU and the USA but the same as the world.
- 2017: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 5.32%, significantly higher than the average inflation rates of the EU, USA, and the world.
- 2016: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 5.17%, higher than the average inflation rates of the EU, USA, and the world.
- 2015: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 5.59%, higher than the average inflation rates of the EU, USA, and the world.
- 2014: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 6.13%, higher than the average inflation rates of the EU, USA, and the world.
- 2013: Tanzania’s inflation rate was 7.87%, significantly higher than the average inflation rates of the EU, USA, and the world.
Conclusion
Although Tanzania has experienced inflation rates higher than the EU average and occasionally above the global average, it has consistently achieved lower inflation rates than the United States in the last 10 years. It is essential to recognize that various factors, such as economic conditions, monetary policies, fiscal policies, and external influences, shape inflation rates.
Through prudent monetary policies, a stable exchange rate, controlled food inflation, stable oil prices, and fiscal discipline, Tanzania has successfully managed to keep inflation in check, contributing to its economic stability and growth.













